GENERATION 2.0
Inspired to build the world’s leading high-science retina pipeline
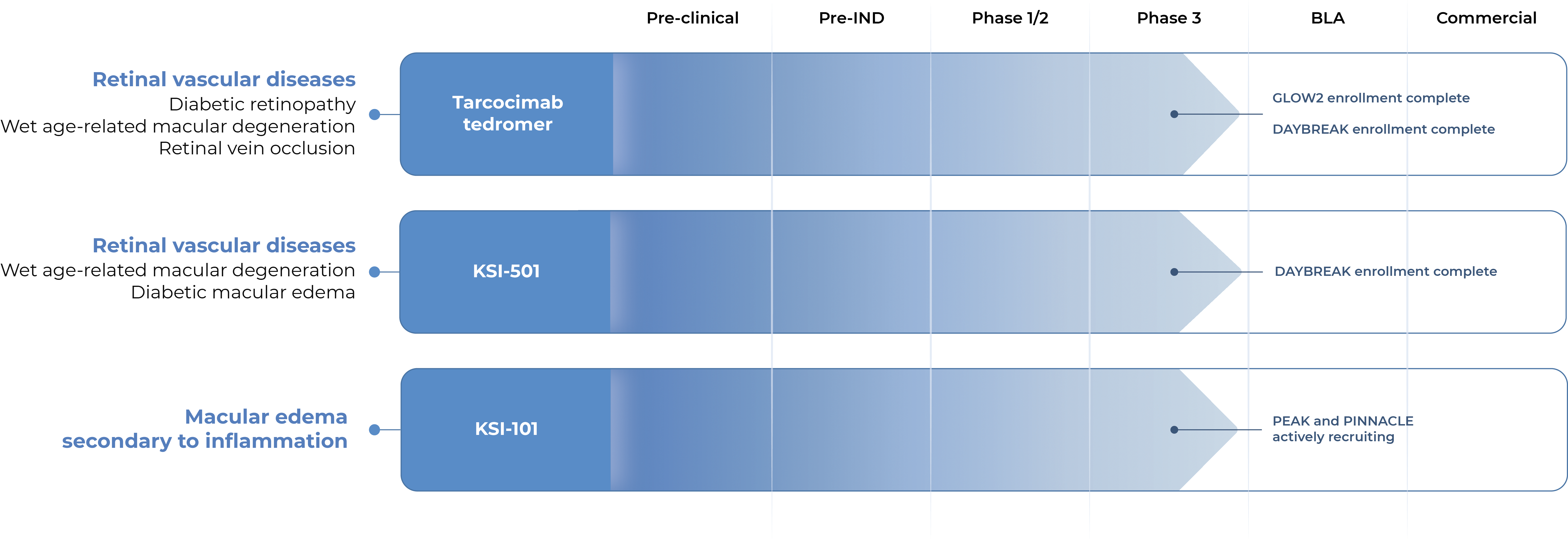
OUR PIPELINE
Our pipeline is designed to address key limitations of today’s therapies across a broad spectrum of retinal diseases.
GLOW2 Enrollment complete
DAYBREAK Enrollment complete
DAYBREAK Enrollment complete
PEAK and PINNACLE actively recruiting
OUR CANDIDATES
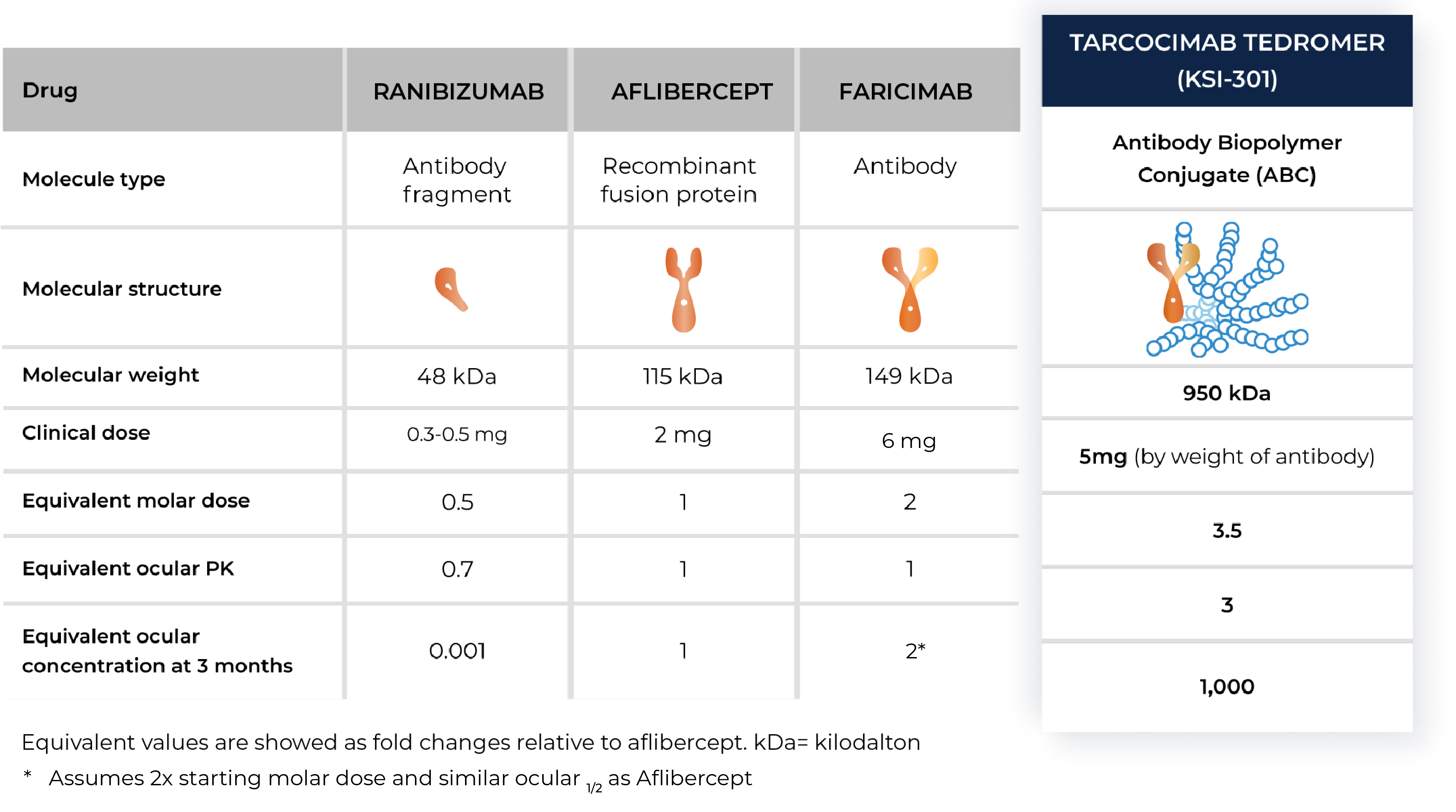
Tarcocimab tedromer
Anti-VEGF
KSI-501
Anti-IL-6, VEGF trap

KSI-101
Anti-IL-6, VEGF trap

Multi-mechanistic medicines
1 Molecule, Many targets
An investigational anti-VEGF biologic designed
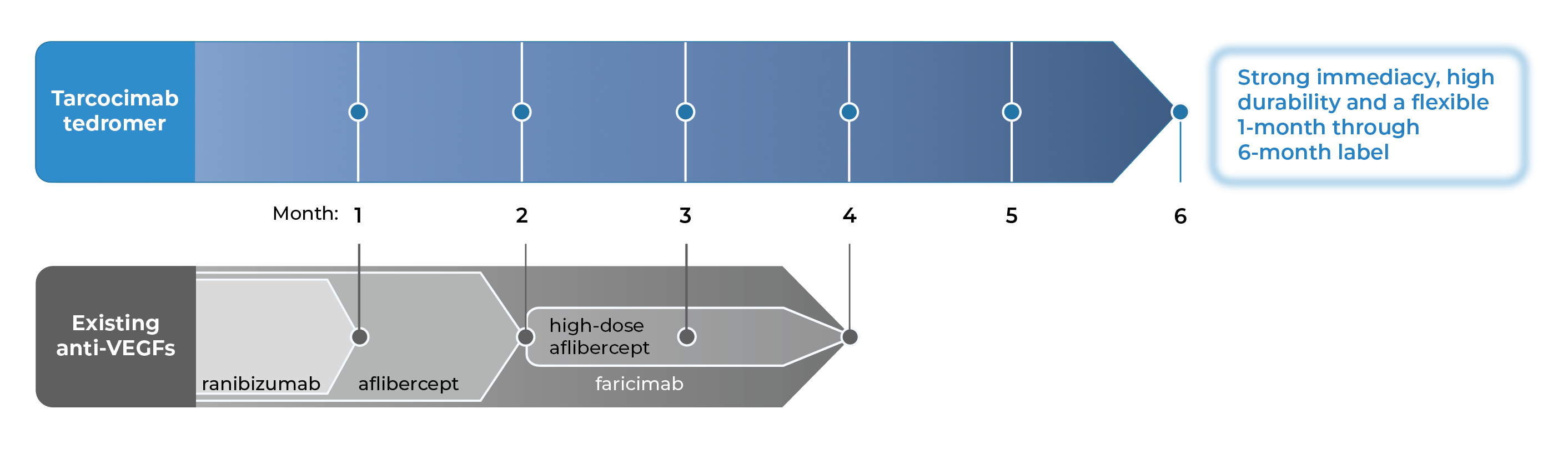
for strong immediacy and high durability
Tarcocimab is our most advanced program with three Phase 3 studies complete and two ongoing.
Tarcocimab is an anti-VEGF Antibody Biopolymer Conjugate (ABC) being developed to provide strong immediacy and high durability. Across multiple studies in high-prevalence retinal vascular diseases, tarcocimab demonstrated consistent 6-month predominant durability and favorable safety. With a flexible 1-month through 6-month label, we believe tarcocimab can be the “mainstay” intravitreal biologic for all patients.
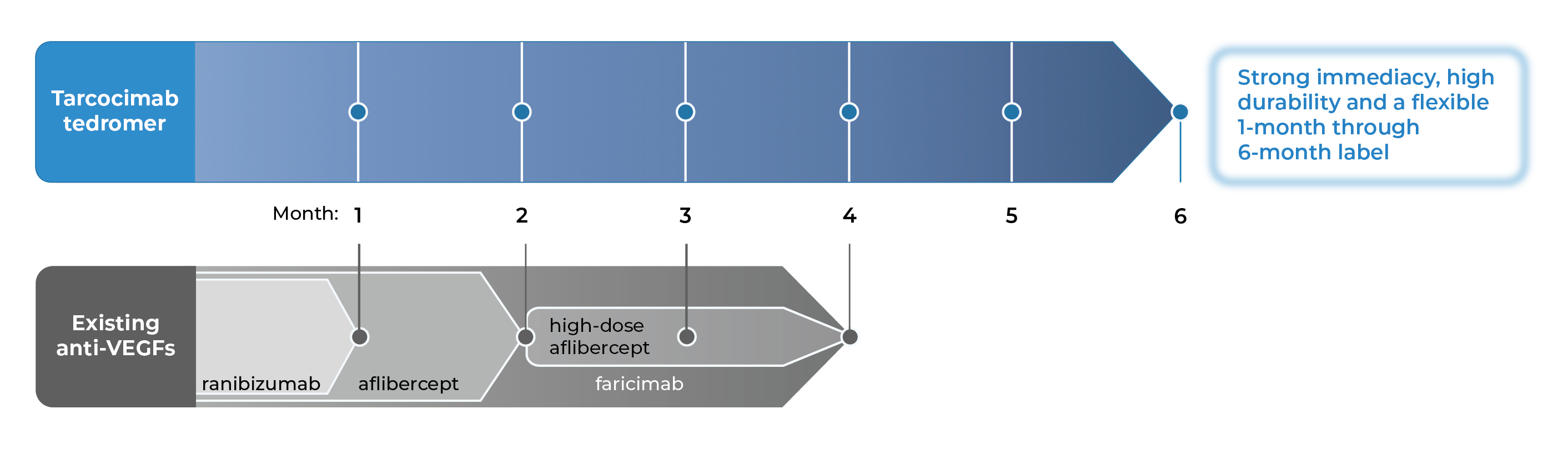
- Across tarcocimab tedromer pivotal studies for diabetic retinopathy, retinal vein occlusion and wet age-related macular degeneration.
- According to the product label for aflibercept, high-dose aflibercept, faricimab and ranibizumab.
The enhanced formulation is engineered for immediate and durable VEGF inhibition
The enhanced formulation of tarcocimab includes unconjugated and conjugated protein in a single biologic. The unconjugated protein is designed to deliver a strong “pulse” of VEGF inhibition and the conjugated protein is designed to persist in the eye to provide sustained disease control.

Tarcocimab and the Science of Durability
Tarcocimab is an ABC medicine built to last. This designed-in durability is supported by clinical data and is what we call our science of durability. See the data
Tarcocimab and the Science of Durability
Tarcocimab is an ABC medicine built to last. This designed-in durability is supported by clinical data and is what we call our science of durability. See the data
Our Phase 3 studies across high-prevalence retinal diseases
Three Phase 3 studies complete in three major retinal diseases. Primary endpoint met and compelling durability demonstrated.
| Study Design | Primary Endpoint | Extended Durability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLOW1 Study Diabetic Retinopathy |
|
✓ | ✓ | See Results |
| BEACON Study Retinal Vein Occlusion |
|
✓ | ✓ | See Results |
| DAYLIGHT Study Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration |
|
✓ | Not Applicable | See Results |
In addition to these studies, tarcocimab was also studied in the Phase 2b/3 DAZZLE study in wet AMD and in the Phase 3 GLEAM and GLIMMER studies in DME. These studies did not meet primary endpoint but did demonstrate strong 5 and 6-month durability in the majority of patients.
Two new Phase 3 studies in process using the enhanced formulation of tarcocimab.
| Study Design | Primary Endpoint | Anticipated Timing | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLOW2 Study Diabetic Retinopathy |
|
Topline data expected Q1 2026 | See Results | |
| DAYBREAK Study Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration |
|
Topline data expected Q3 2026 | See Results |
Our objective is for tarcocimab to be a “mainstay” intravitreal biologic monotherapy that provides high efficacy and high durability for all patients
Results from our Phase 3 clinical studies
Tarcocimab demonstrated differentiated durability in the GLOW1 study in diabetic retinopathy and in the BEACON study in retinal vein occlusion.
GLOW1 Phase 3 study in diabetic retinopathy1
- Patients treated with tarcocimab received only 4 injections in Year 1
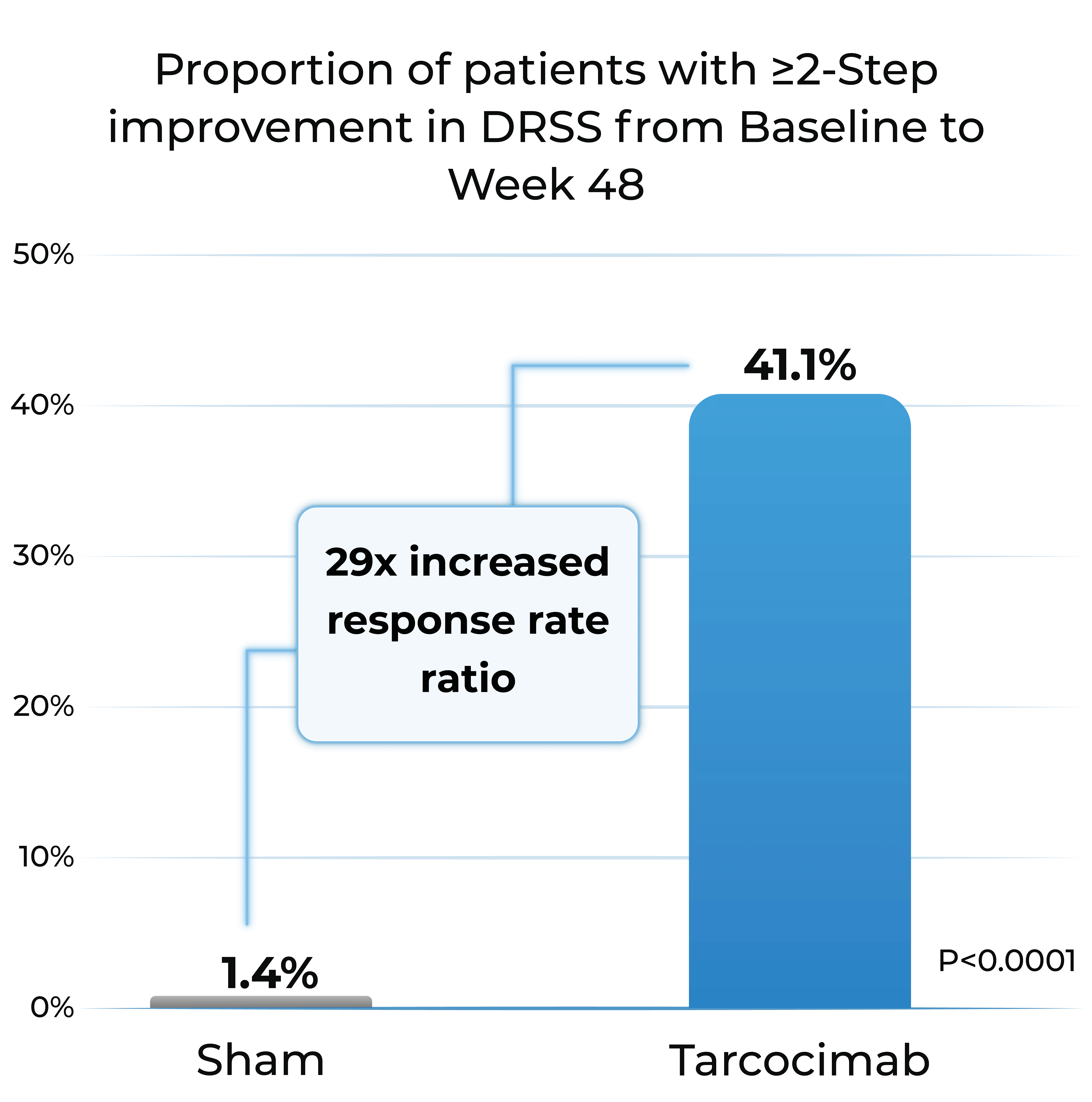
- Tarcocimab demonstrated superiority in ≥2-step and ≥3-step improvement in DRSS
Proportion of patients with ≥2-Step improvement in DRSS from Baseline to Week 48
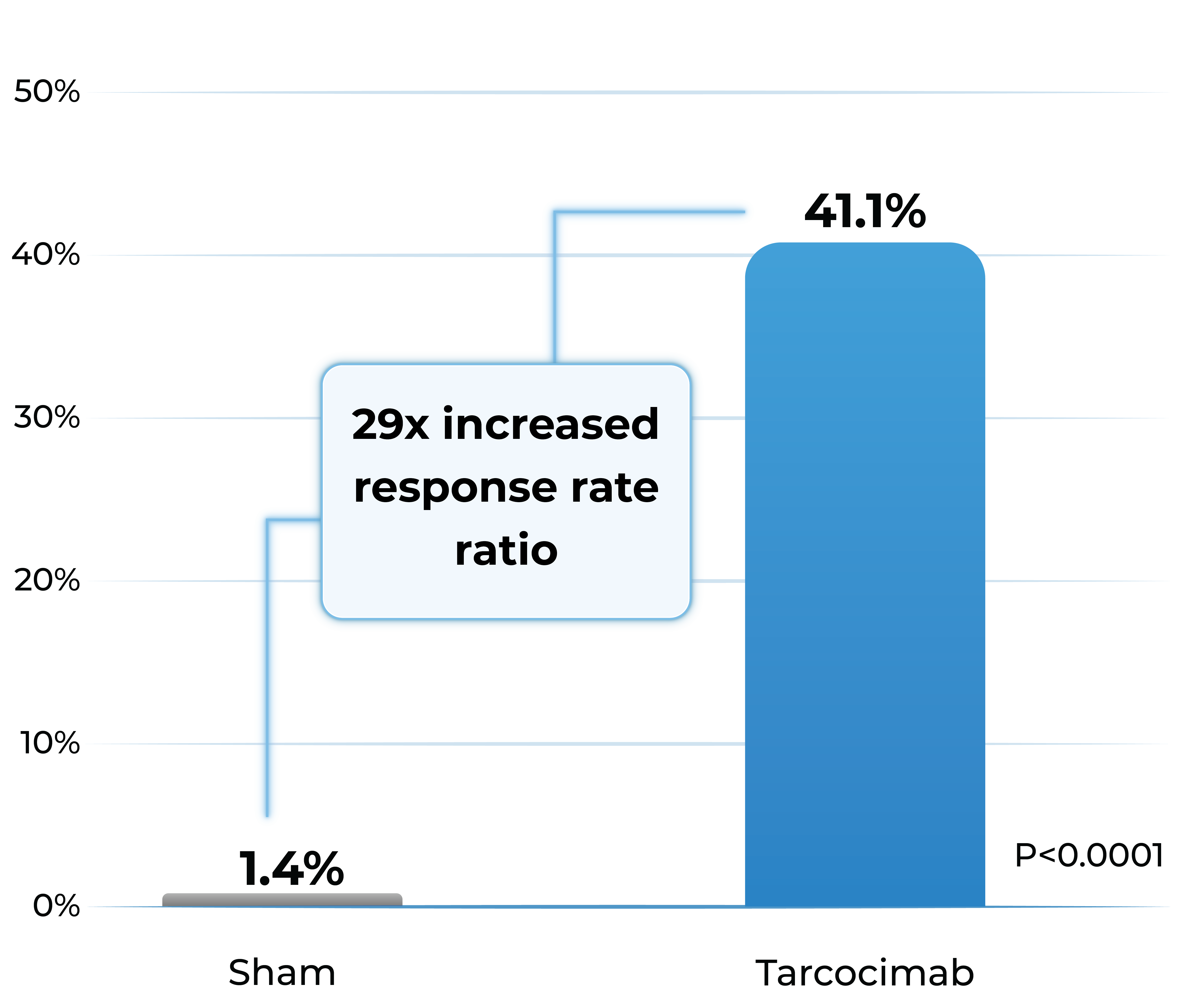
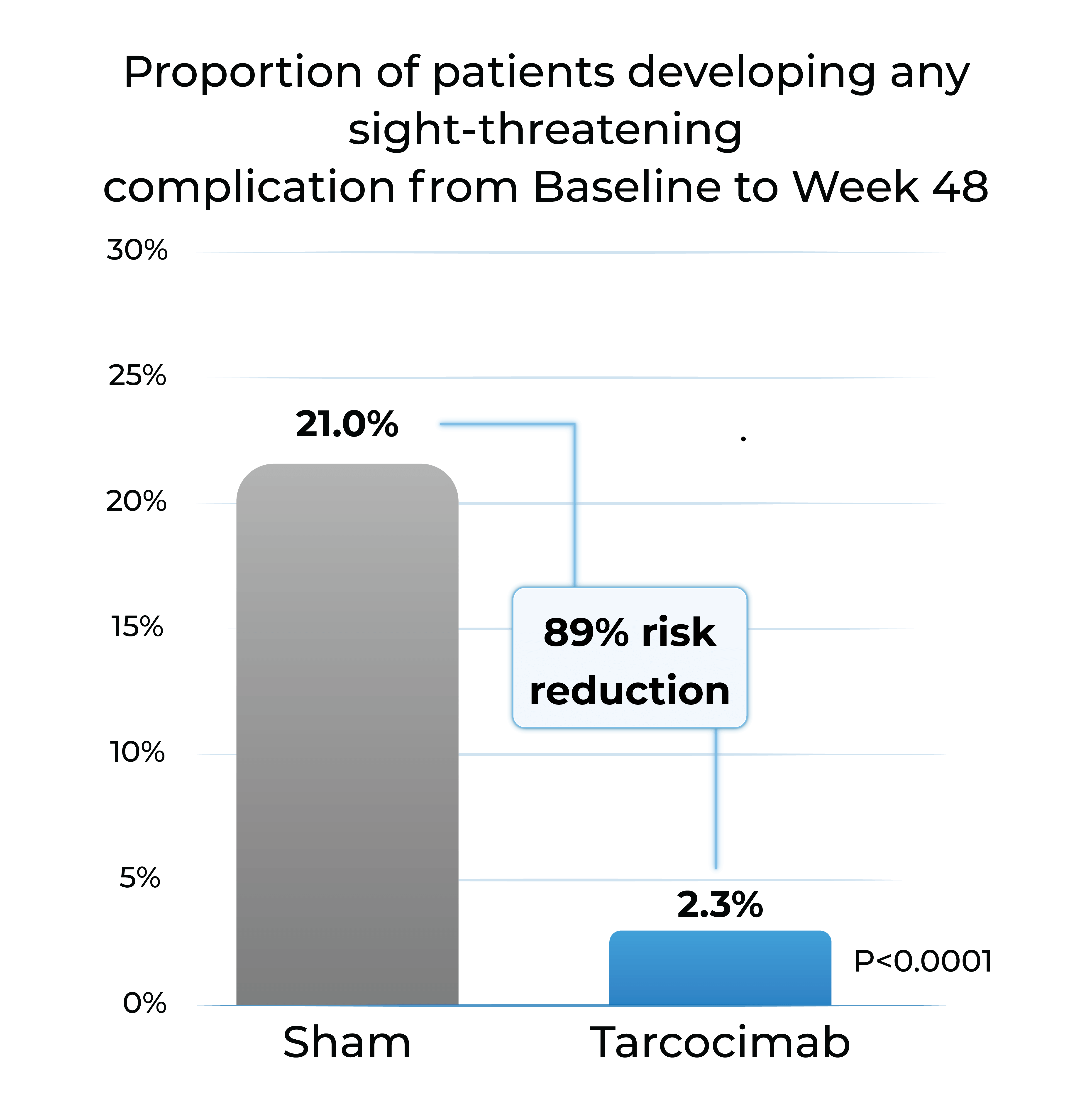
Proportion of patients developing any sight-threatening complication from Baseline to Week 48
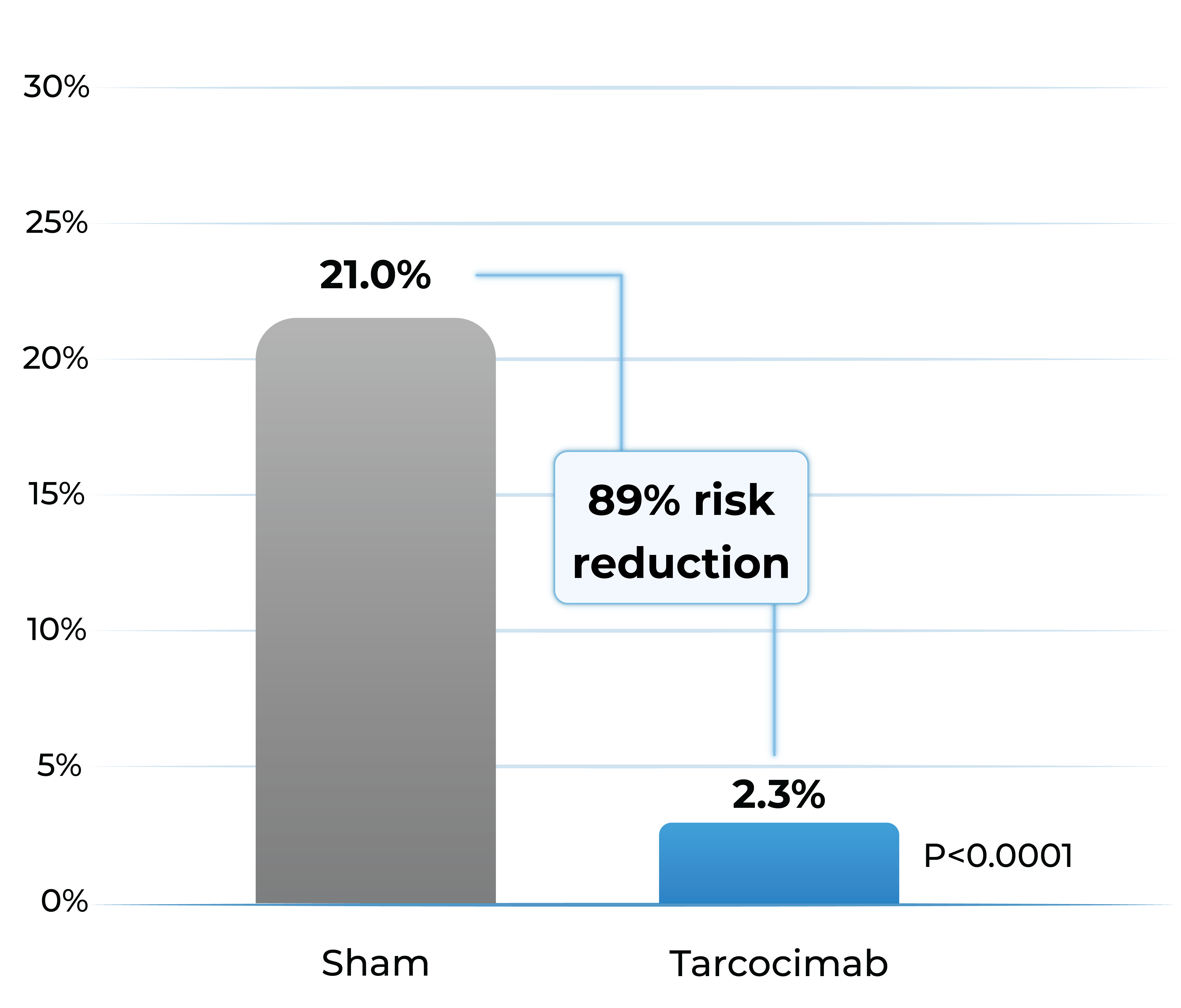
- Tarcocimab reduced the risk of developing a pre-specified sight-threatening complication by ~90%
Any Sight-Threatening Complication
| DME | CST of ≥320 and a 5-letter decrease in BCVA from Day 1; or CST of ≥350 |
| PDR | NVD or NVE, or VH |
| ASNV | ASNV or NVG |
1. The Phase 3 GLOW1 study is a global, multi-center, randomized pivotal study designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of tarcocimab in patients with treatment-naïve, moderately severe to severe DR. All patients were randomized to receive either tarcocimab every six months after 3 initiating doses or to receive sham injections.
DRSS: diabetic retinopathy severity scale; DME; diabetic macular edema; PDR; proliferative diabetic retinopathy; ASNV: anterior segment neovascularization; CST; central subfield thickness; BCVA; best corrected visual acuity; NVD: neovascularization of the disc; NVE; neovascularization elsewhere; VH: vitreous hemorrhage; NVG; neovascular glaucoma. Weighted percentages are based on weighted average of observed estimates across strata using CMH weights. p-values are based on the difference in response rates.
BEACON Phase 3 study in retinal vein occlusion2
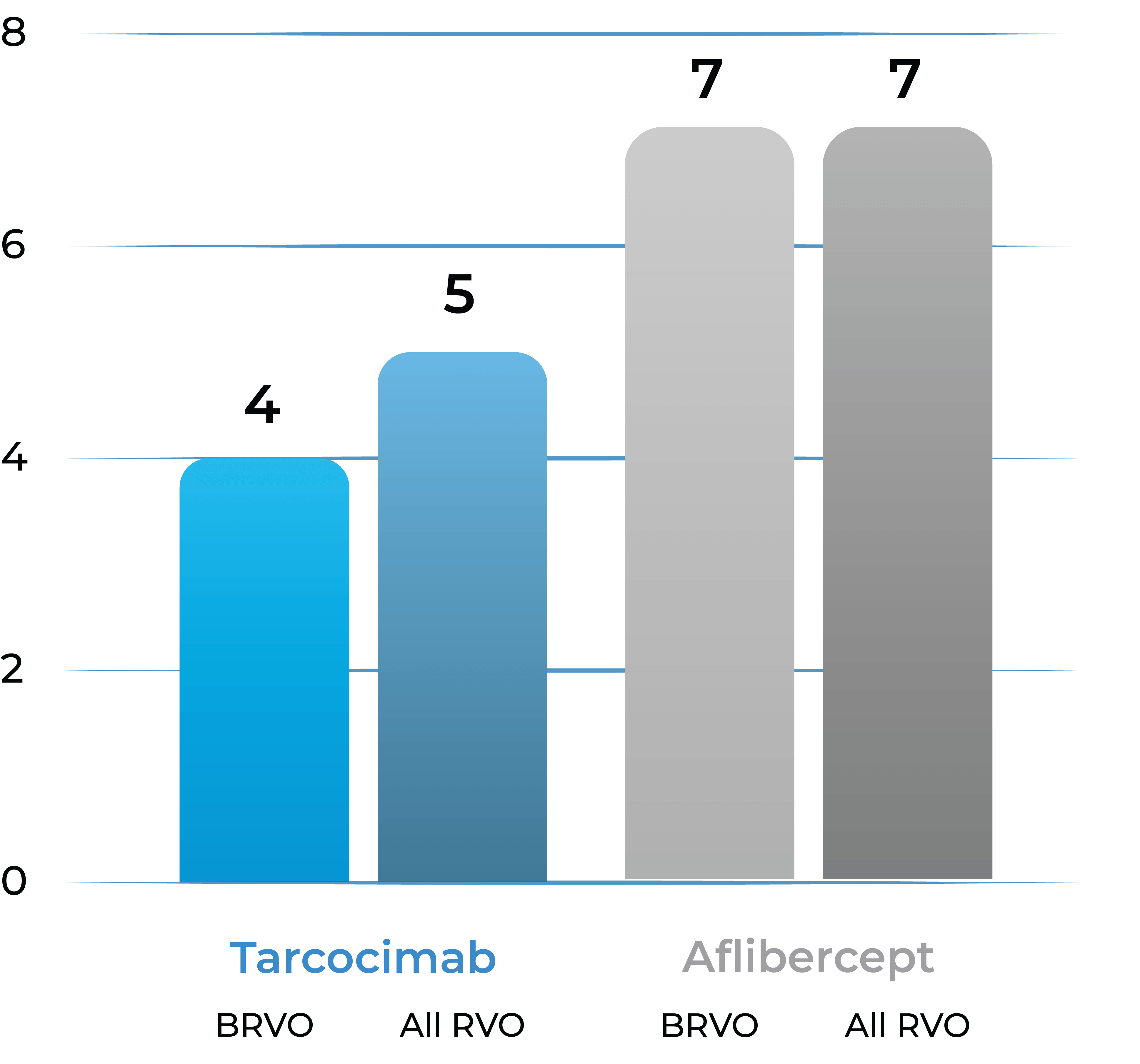
- Tarcocimab Q8W was non-inferior to aflibercept Q4W in all RVO patients at 6 months, thereby doubling the treatment interval
- Approximately half of tarcocimab-treated patients were injection free in the second 6 months of the study
- Despite fewer injections in tarcocimab-treated patients, vision outcomes at Year 1 favored tarcocimab-treated patients achieving an observed mean of 74.6 letters versus 74.3 letters for aflibercept-treated patients
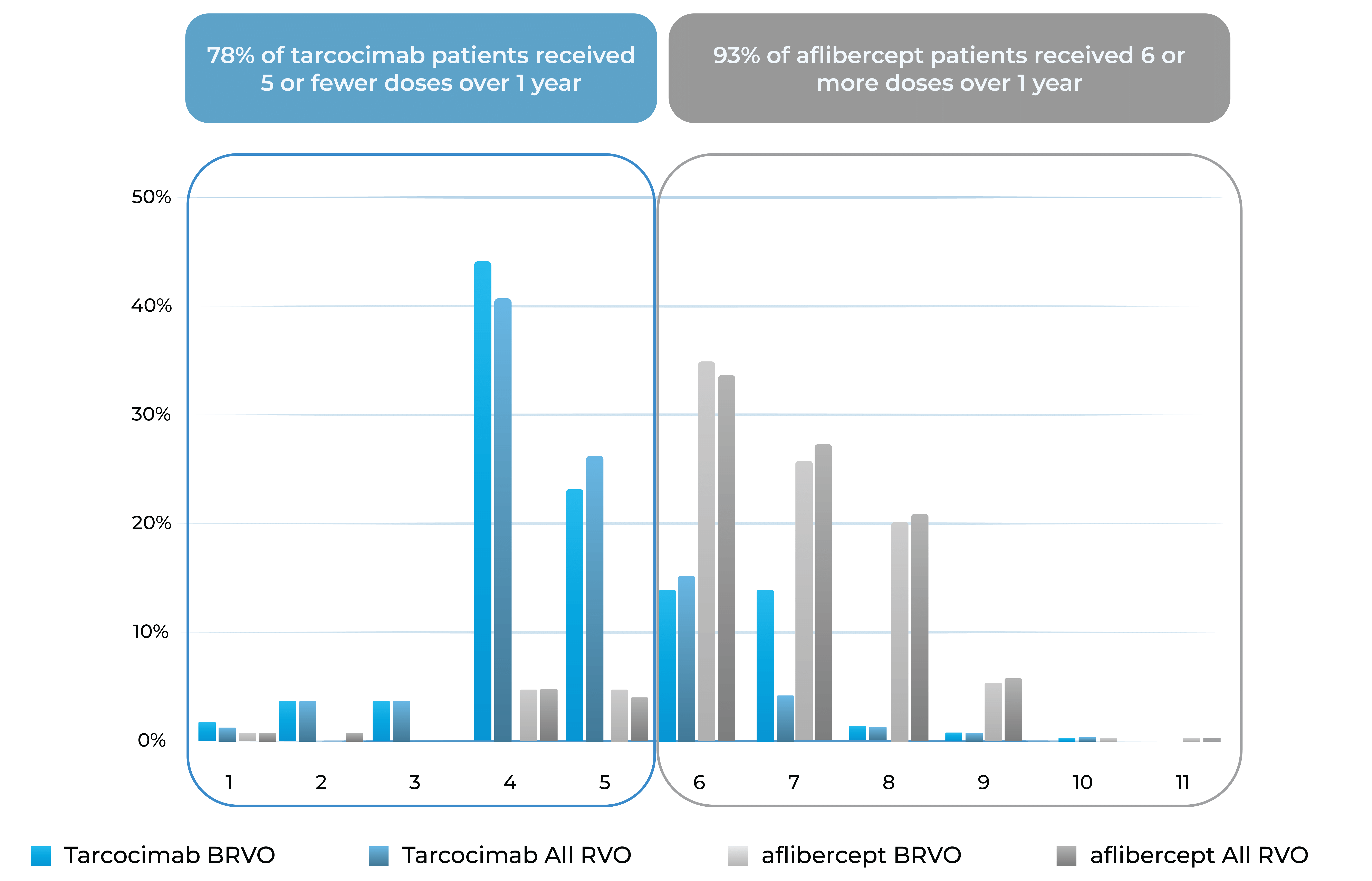
Median number of injections through Week 48
Treatment distribution through Week 48
78% of tarcocimab patients received 5 or fewer doses over 1 year
93% of aflibercept patients received 6 or more doses over 1 year
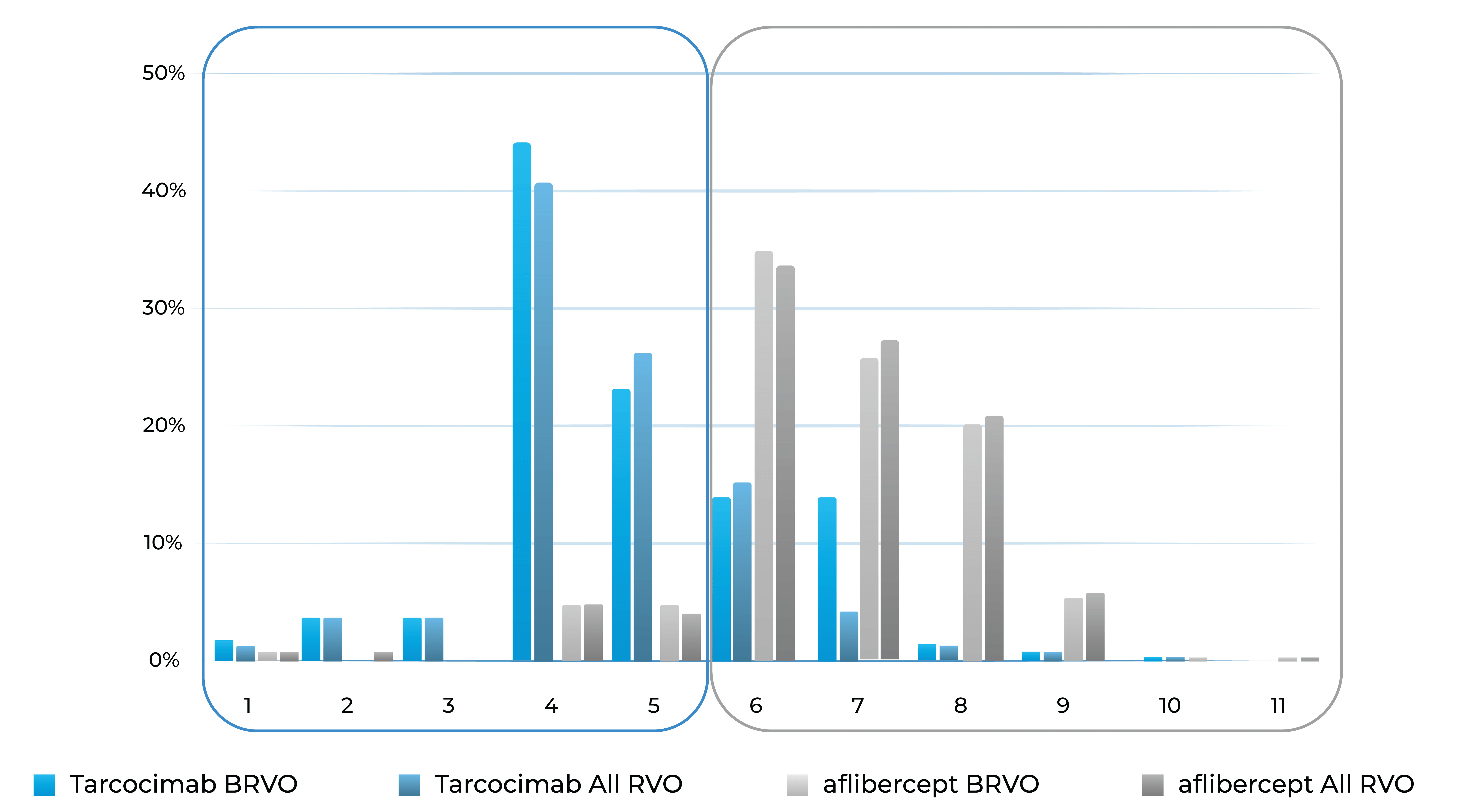
Treatment burden distribution through 48 weeks had minimal overlap, favoring tarcocimab in both BRVO and All RVO patients
2. The Phase 3 BEACON study is a global, multi-center, randomized study designed to evaluate the durability, efficacy and safety of tarcocimab tedromer Q8W vs. aflibercept Q4W in patients with macular edema due to RVO.
First-in-class
An investigational anti-IL-6 and VEGF trap bispecific biologic designed for higher efficacy and higher durability
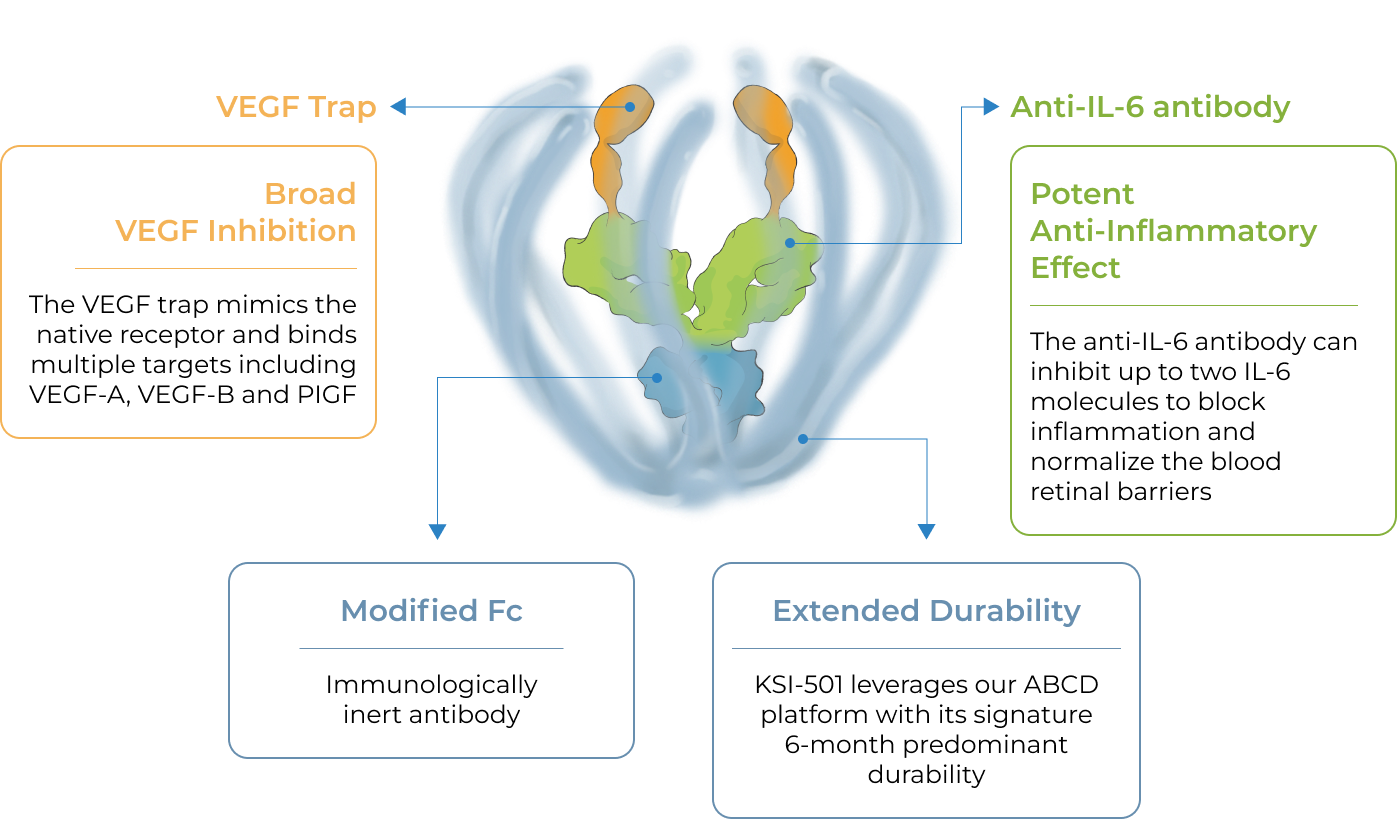
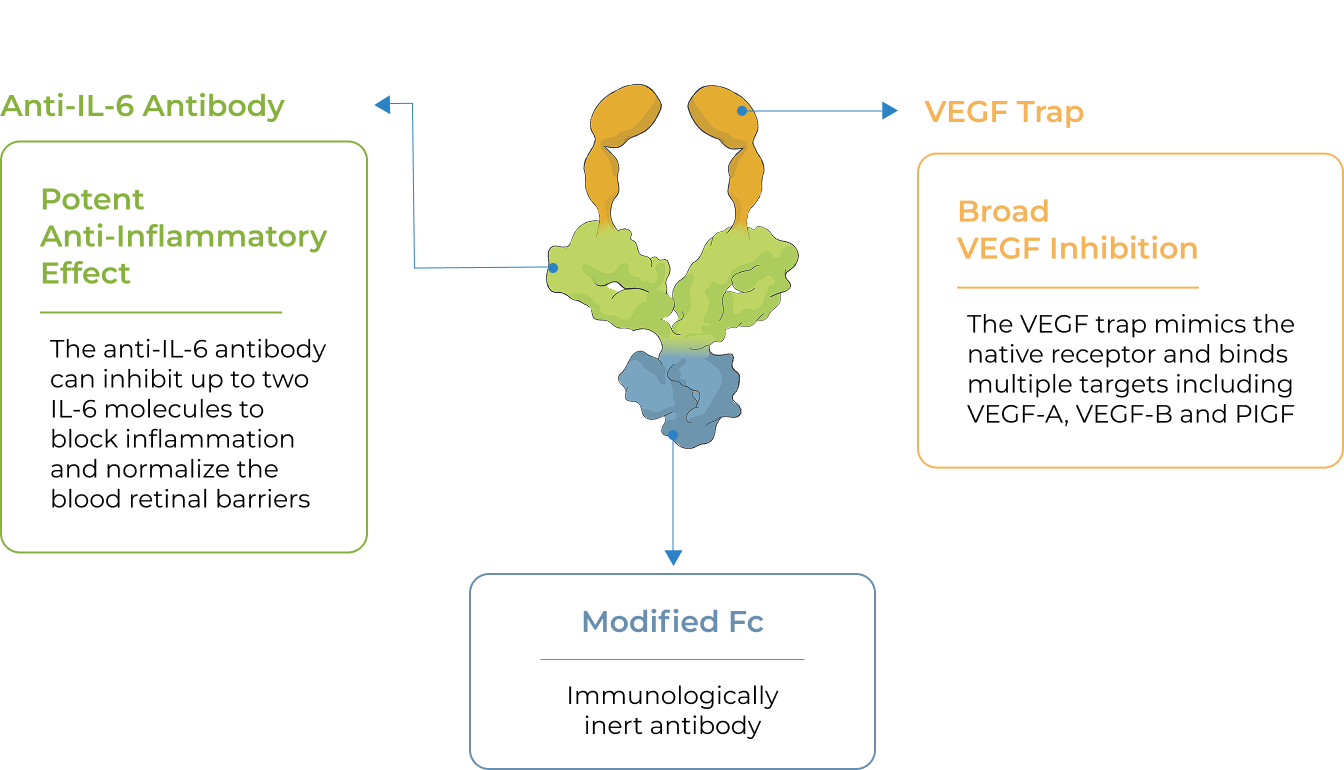
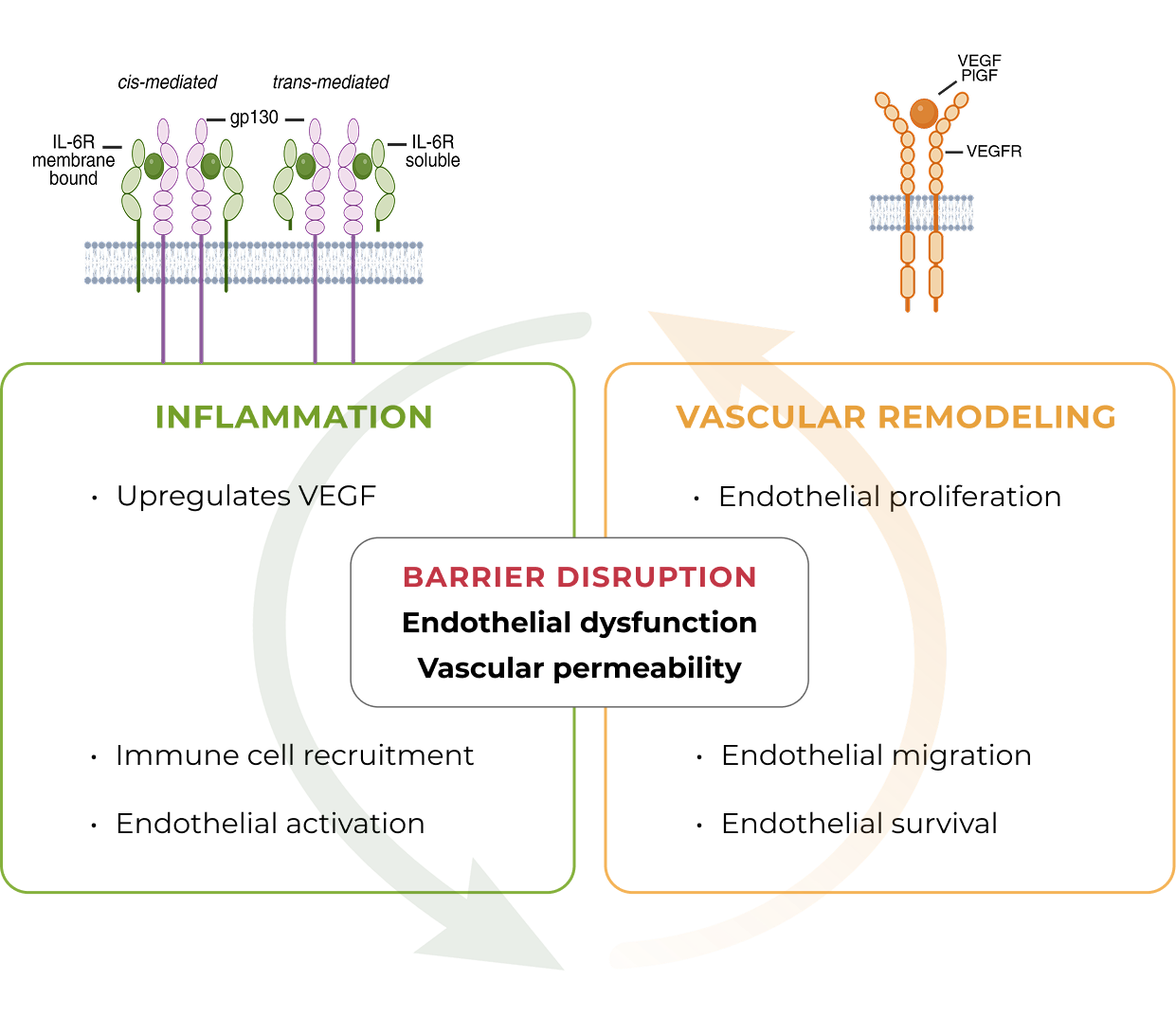
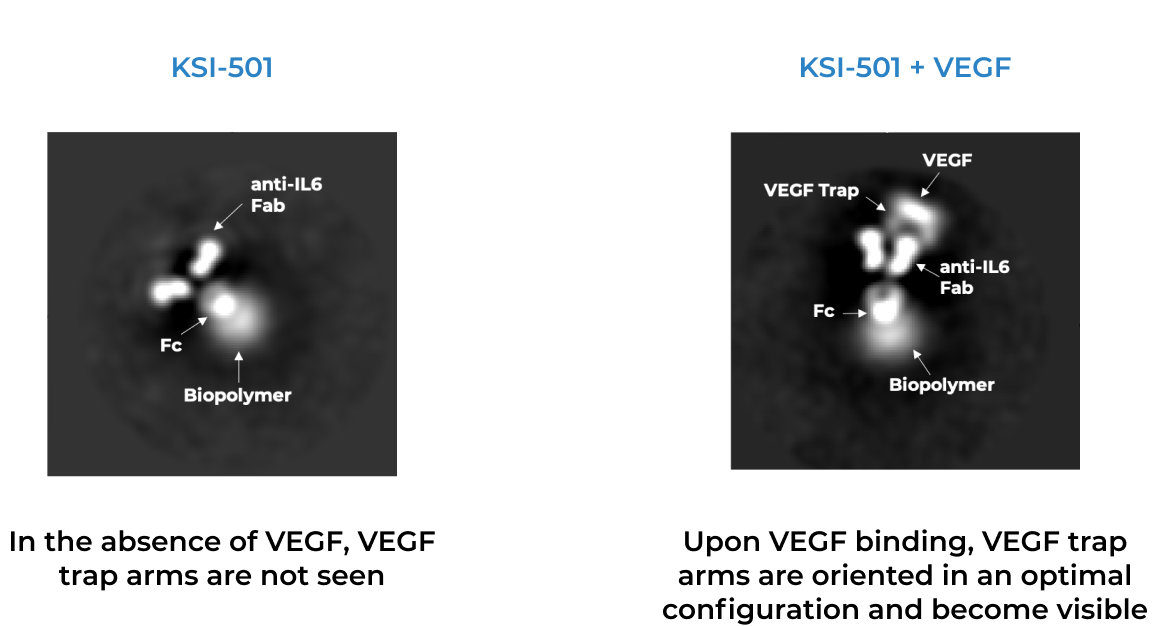
KSI-501 is a bispecific Antibody Biopolymer Conjugate (ABC) designed to address two key unmet needs in high-prevalence retinal vascular diseases – higher efficacy and higher durability – by targeting retinal inflammation and vascular permeability simultaneously.
Inflammation has been shown to play a significant role in high-prevalence retinal vascular diseases. However, no treatments exist that concurrently address vascular permeability and inflammation.
KSI-501 is designed to inhibit VEGF and IL-6, a pro-inflammatory cytokine and immune growth factor, combining two powerful mechanisms of action to address retinal vascular disease and the underlying inflammatory cascade.
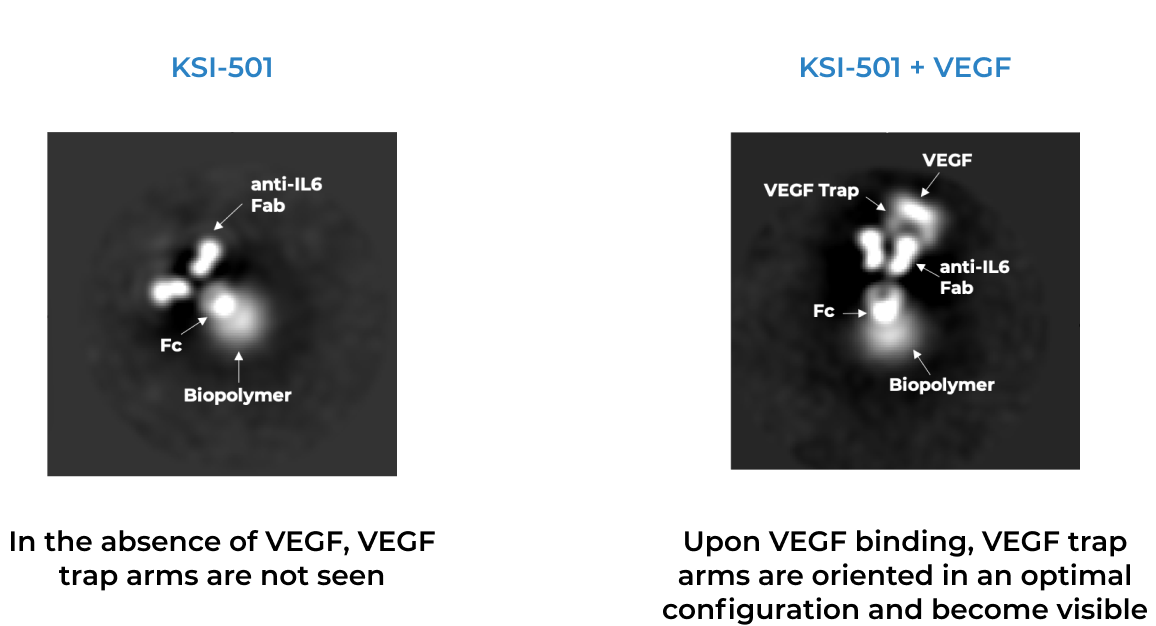
KSI-501 is designed for highly efficient binding to both IL-6 and VEGF
The anti-permeability effect of VEGF inhibition is the primary effector, with the anti-inflammatory effect of IL-6 inhibition offering the potential for additional clinical benefits.
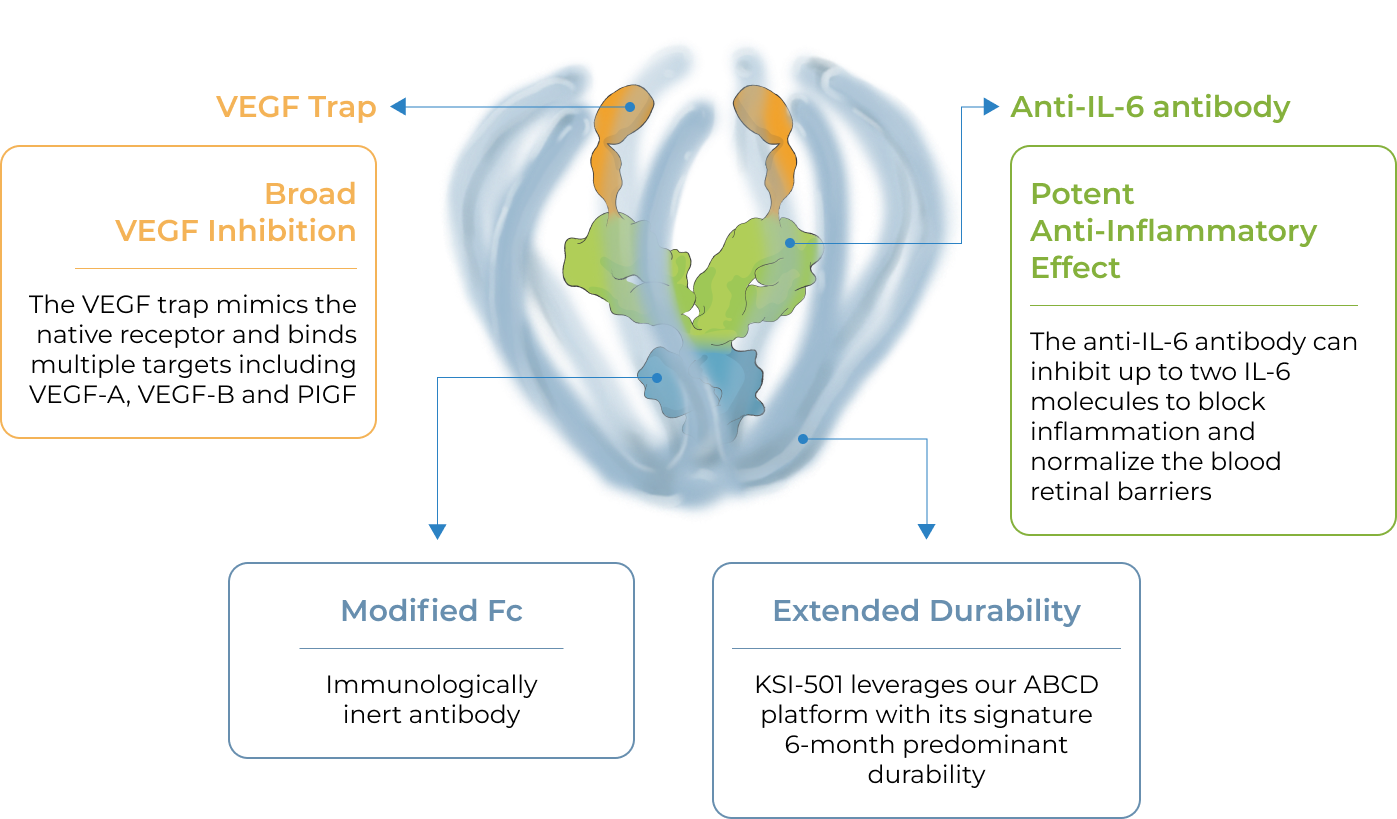
The enhanced formulation is engineered for immediate and durable bispecific inhibition
The enhanced formulation of KSI-501 includes unconjugated and conjugated protein. The unconjugated protein is designed to deliver a strong “pulse” and the conjugated protein is designed to persist in the eye to provide sustained disease control.

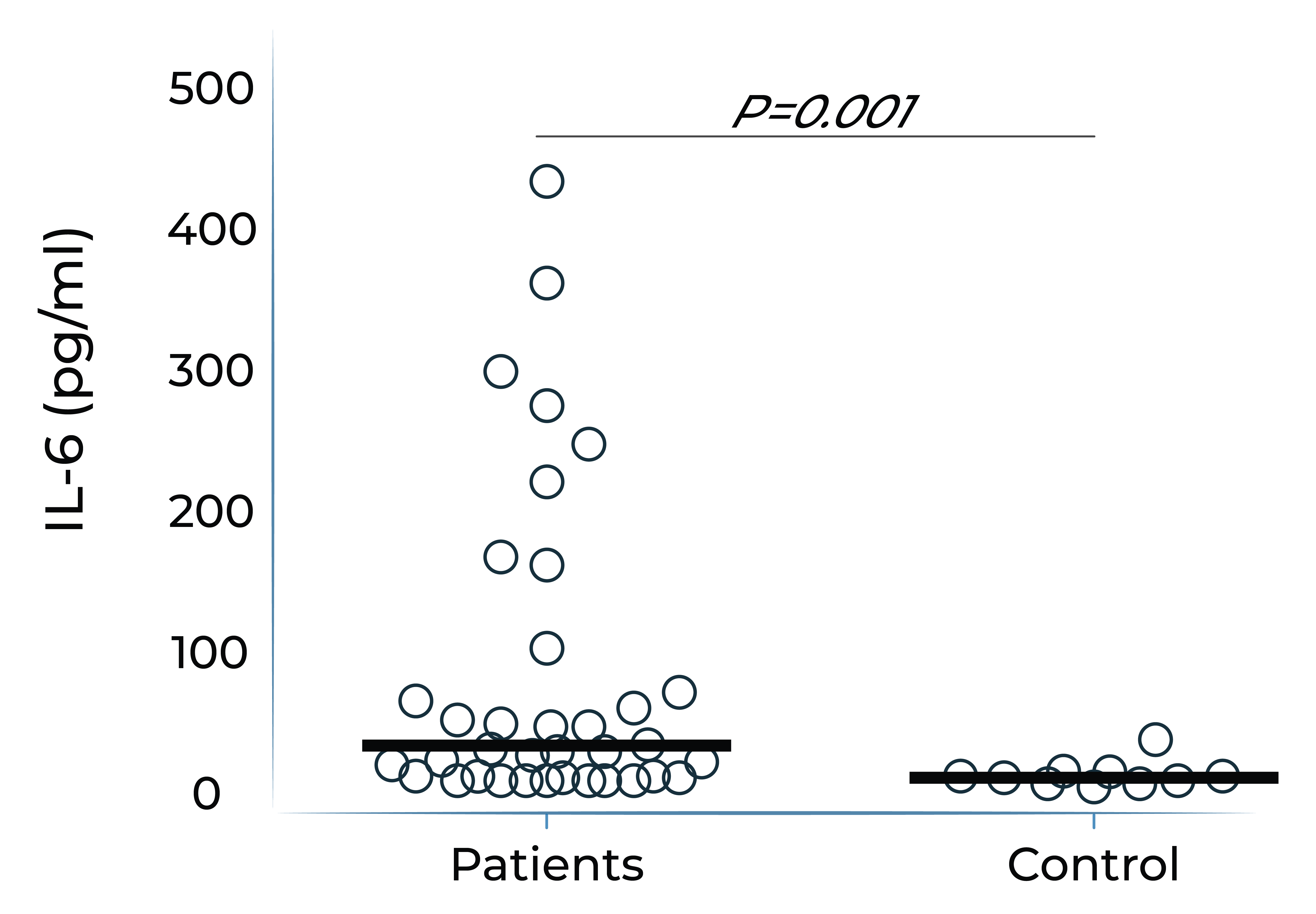
IL-6 levels are significantly elevated in eyes with retinal vascular disease and are implicated in anti-VEGF treatment resistance
Vitreous IL-6 levels in patients with retinal vascular disease vs. control1

DME: diabetic macular edema; PDR: proliferative diabetic retinopathy; BRVO: branch retinal vein occlusion; CRVO: central retinal vein occlusion; RD: retinal detachment.
1.Yoshimura et al. (2009). PLoS ONE 4(12): e8158.
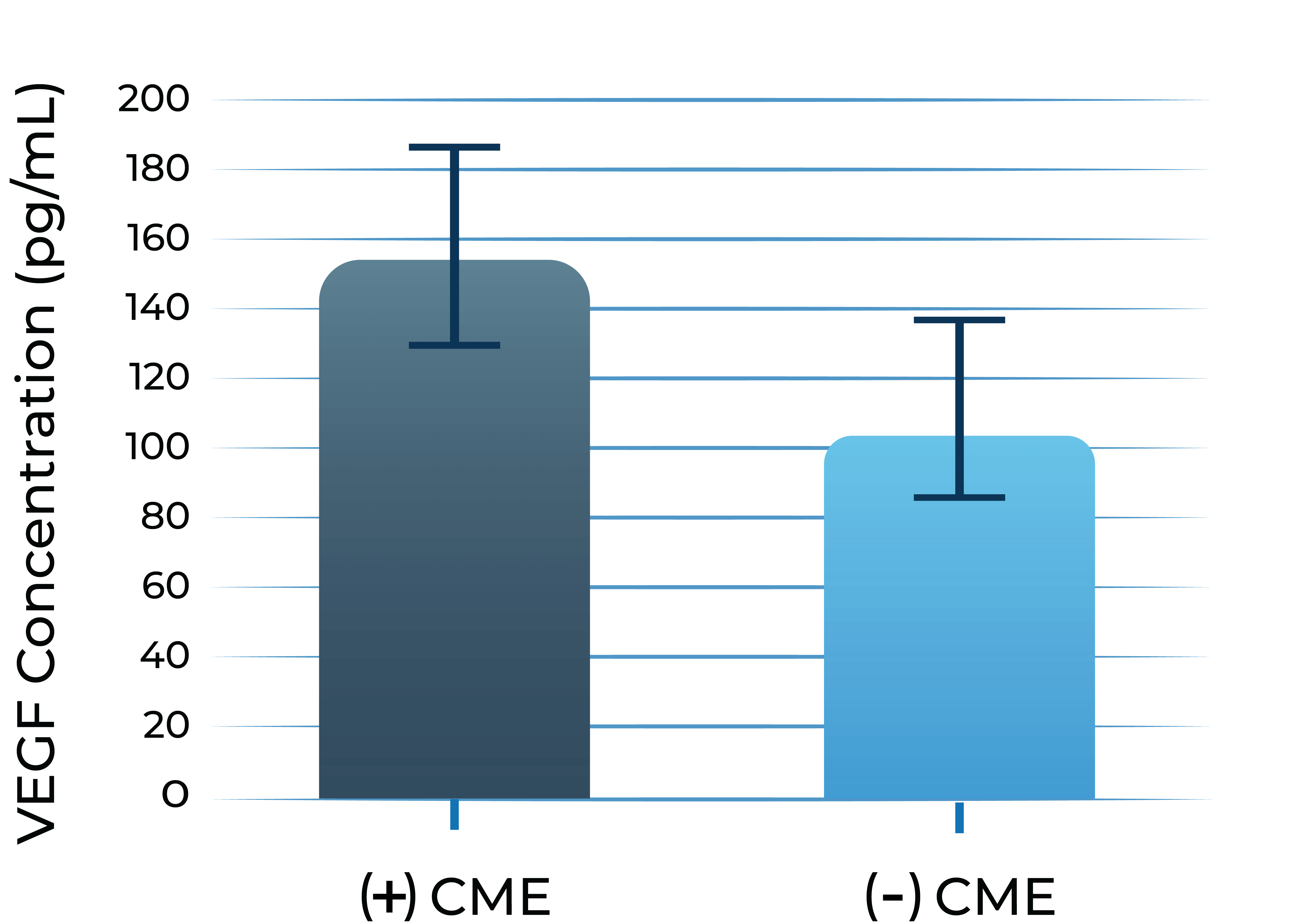
Aqueous humor IL-6 levels in patients with wet AMD at baseline and after anti-VEGF treatment2
Patients that respond to anti-VEGF

Anti-VEGF treatment resistant patients

- Adapted from Chalam et al. (2014). Journal of Ophthalmology, Article ID 502174. Mean with SEM plotted.
Higher aqueous humor IL-6 levels in wet AMD and DME patients treated with anti-VEGF monotherapy correlate with poorer best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) outcomes over time
In pre-clinical studies, dual inhibition of IL-6 and VEGF by KSI-501 show a synergistic effect on barrier biology
Dual inhibition of VEGF and IL-6 by KSI-501 confers superior normalization of complex tight junction-mediated barrier biology compared to either anti-VEGF or anti-IL-6 monotherapy alone demonstrating the synergistic effect of IL-6 and VEGF dual inhibition on retinal vascular disease.

Dual inhibition of VEGF and IL-6 by KSI-501 confers superior normalization of complex tight junction-mediated barrier biology compared to either anti-VEGF or anti-IL-6 monotherapy alone
With dual effect on the blood retinal barrier, KSI-501 holds the potential to be a new disease-modifying therapy
Phase 3 DAYBREAK study of KSI-501 in wet AMD
KSI-501 is being investigated in the ongoing Phase 3 DAYBREAK study in wet AMD. The DAYBREAK study is designed to explore the efficacy potential of bispecific IL-6 and VEGF inhibition in fixed Q8W with individualized monthly dosing of KSI-501.
DAYBREAK Study
Wet Age-Related
Macular Degeneration
- Designed as a registrational study for both tarcocimab and KSI-501
- Tarcocimab objective: assess 6-month durability potential with individualized Q4W-Q24W dosing
- KSI-501 objective: explore efficacy potential of bispecific IL-6 and VEGF inhibition in fixed Q8W dosing with additional individualized monthly dosing
- Uses enhanced 50 mg/mL formulation
In wet AMD, there is preclinical evidence that IL-6 is implicated in the development of choroidal neovascularization and clinical evidence demonstrating that IL-6 is associated with development and progression of AMD, resistance to anti-VEGF treatment in wet AMD, and reactivation of disease by promoting growth of new neovascular membranes.
DAYBREAK follows the encouraging results of the Phase 1 study of KSI-501 in DME, a disease known to have high levels of cytokine-mediated microvascular inflammation in addition to VEGF-mediated vascular permeability.
Phase 1
Diabetic Macular
Edema
- 16 patients
- Multiple ascending dose design
- Each patient received 3 monthly doses (Day 1, Week 4 and Week 8) and was followed for 24 weeks total
KSI-501 has three tiers of innovation
Two-target
mechanism of action
![]()
Designed to address two key unmet needs: higher efficacy and higher durability by inhibiting the IL-6 inflammation pathway and the dominant VEGF pathway
Enhanced
formulation
![]()
Enhanced 50 mg/mL formulation is designed to deliver both strong immediacy and high durability
Science of
durability
![]()
Supported by our science of durability
First-in-class
An investigational, high-strength, bispecific protein designed to treat macular edema secondary to inflammation (MESI) for which no approved intravitreal biologic exists today
KSI-101 is a high-strength (100 mg/ml), locally administered, bispecific biologic designed to simultaneously target the two disease drivers of MESI – IL-6-mediated inflammation and VEGF-mediated vascular permeability
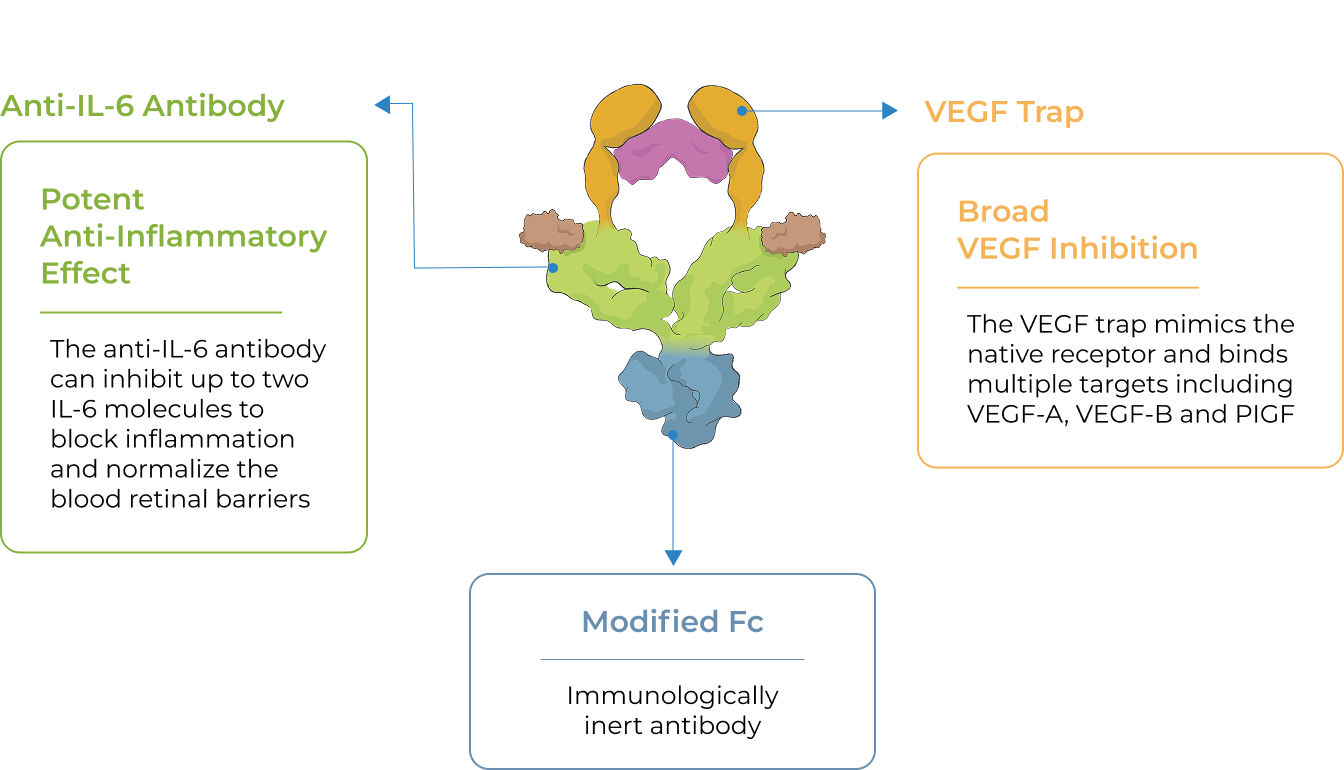
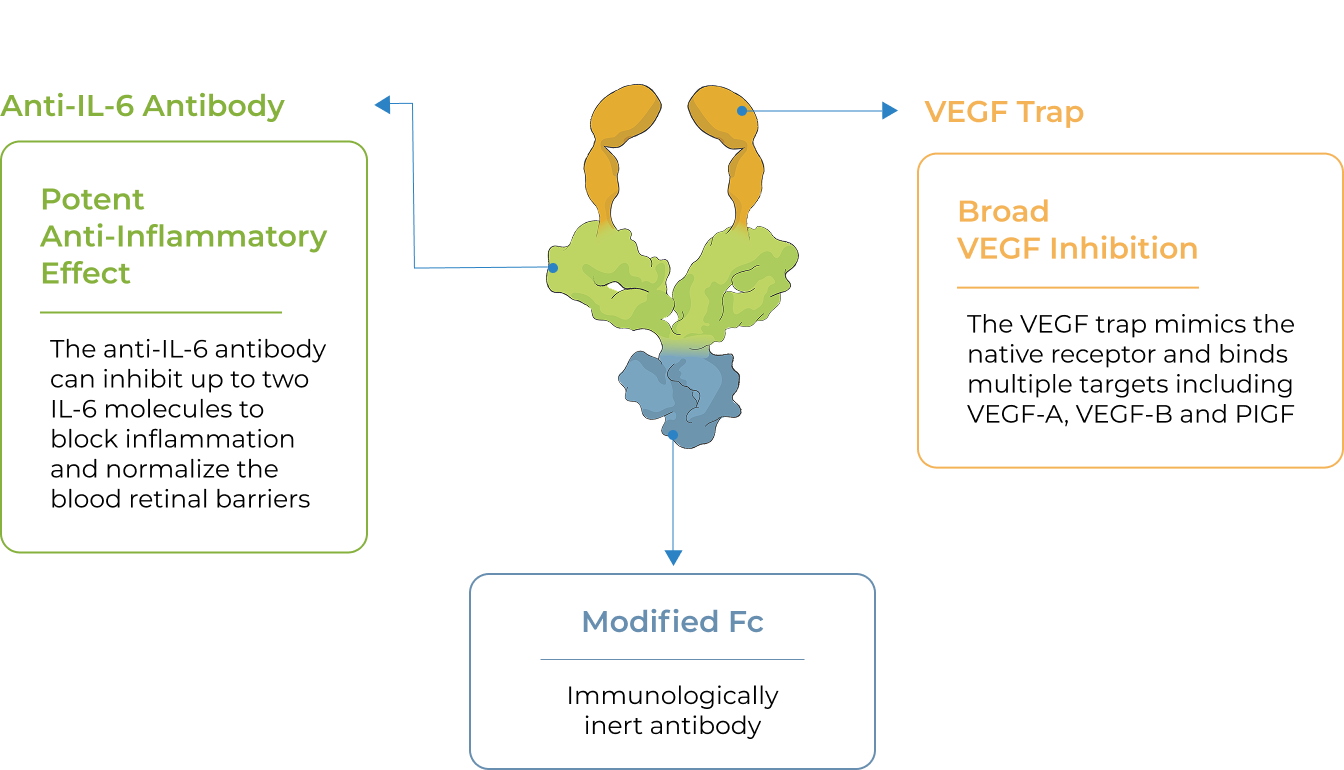
The unique promise of KSI-101 supported by emerging clinical data
Bispecific
KSI-101 targets both IL-6 and VEGF
Rapid and Powerful Drying Effect
In the Phase 1b APEX study in MESI, meaningful vision gains were rapidly achieved as early as Week 4. Over 90% of patients achieved retinal dryness by Week 8. Learn more
Favorable Early Clinical Safety Profile
In the Phase 1b APEX study in MESI, KSI-101 was well tolerated at all dose levels. The top two dose levels (5 mg and 10 mg) were selected to advance into the Phase 3 program. Learn more
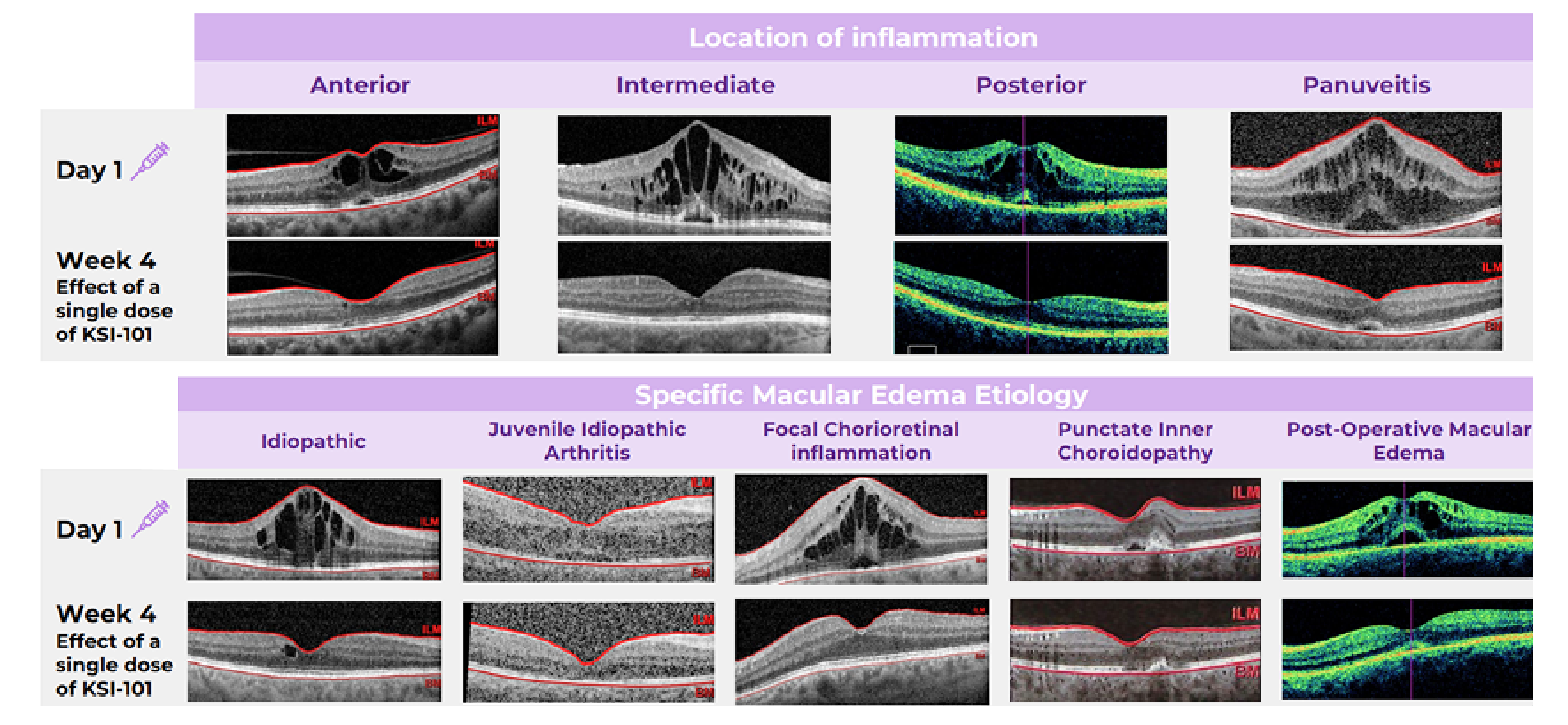
Broad Activity Across MESI Patients
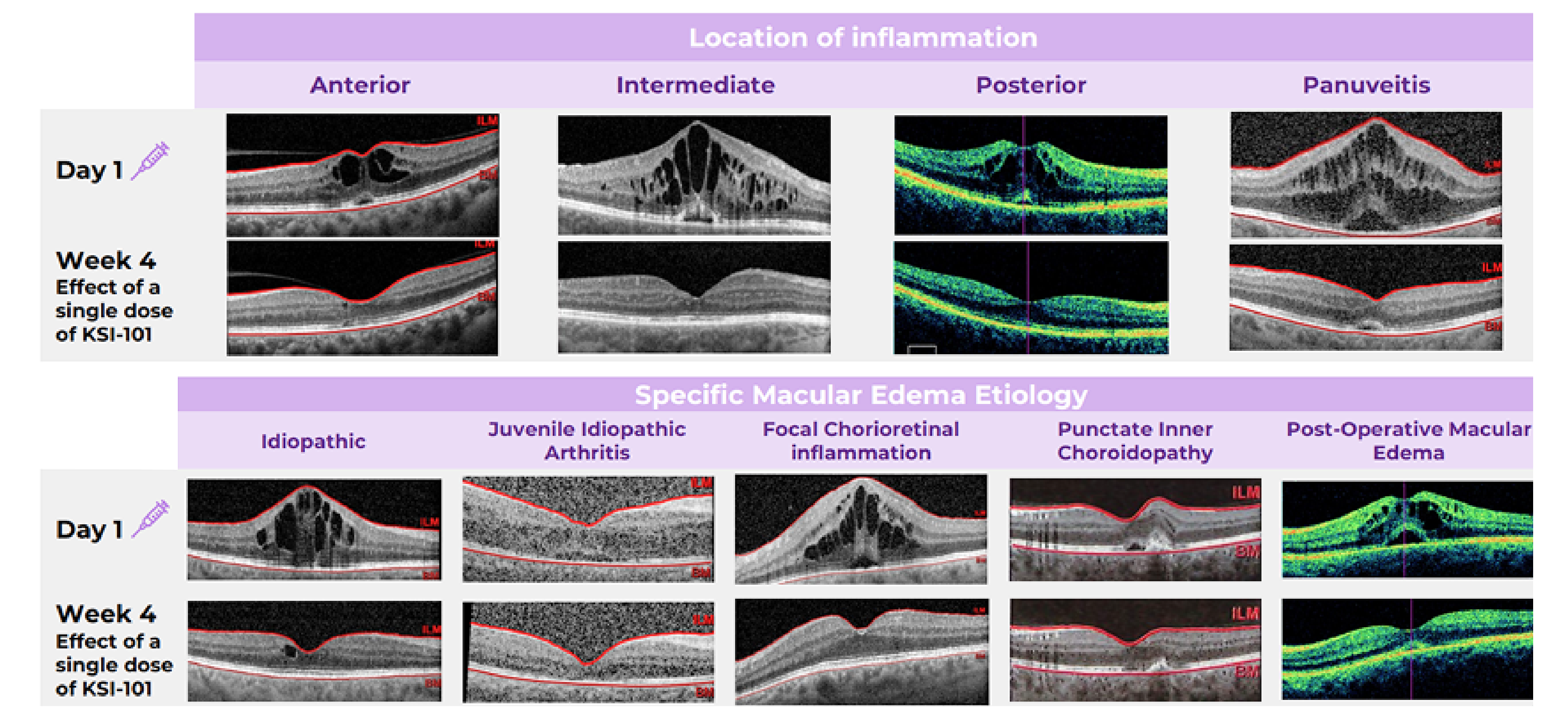
KSI-101 demonstrated rapid and meaningful responses irrespective of the location of inflammation or the specific macular edema diagnosis. Learn more
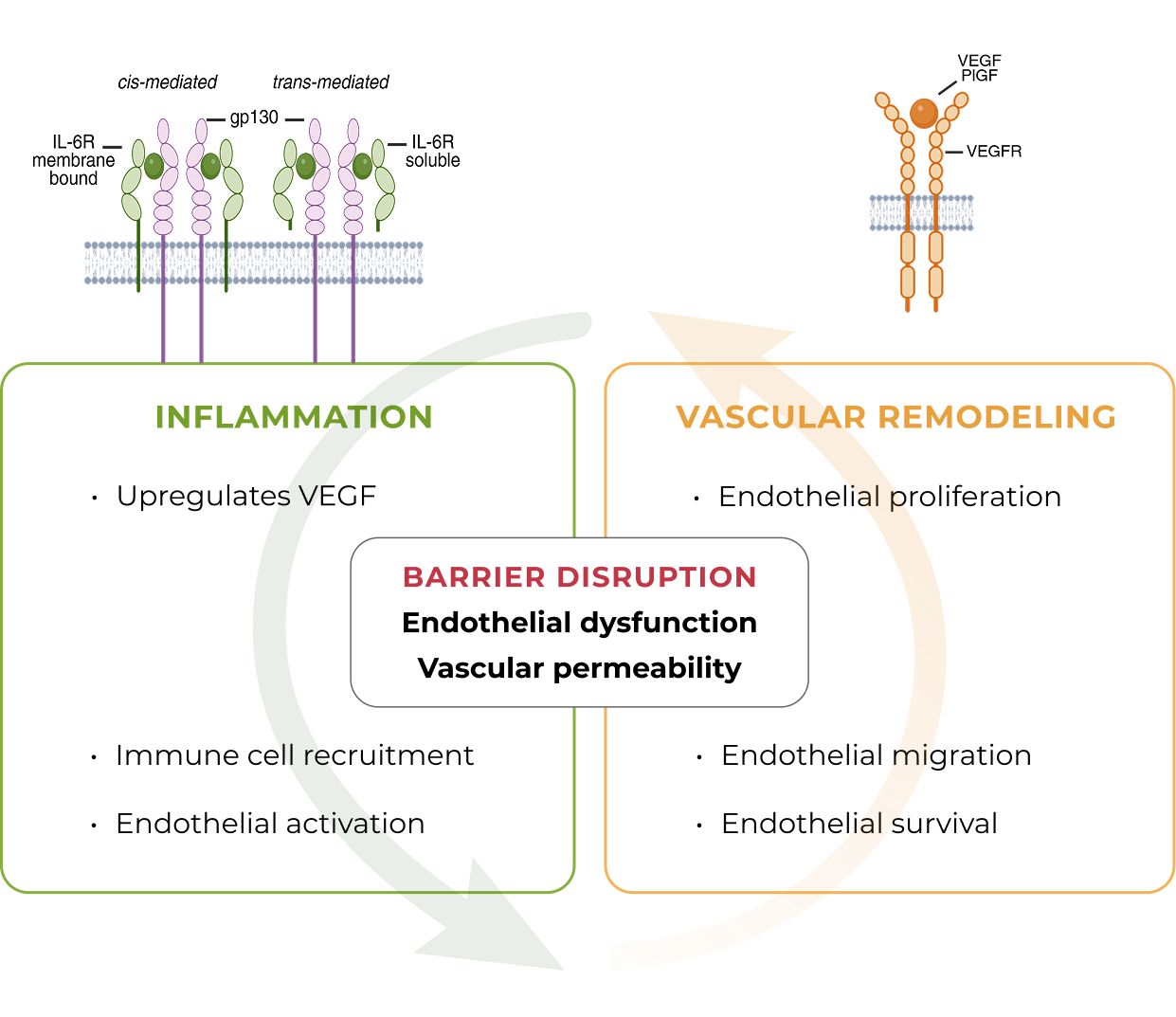
In MESI, IL-6 and VEGF act together to worsen damage to the blood-retinal barrier and increase vascular permeability
MESI occurs when an immune trigger (such as an autoimmune disease) disrupts the blood-retinal barrier, allowing immune cells and blood plasma into the retina, causing inflammation, leakage and macular edema
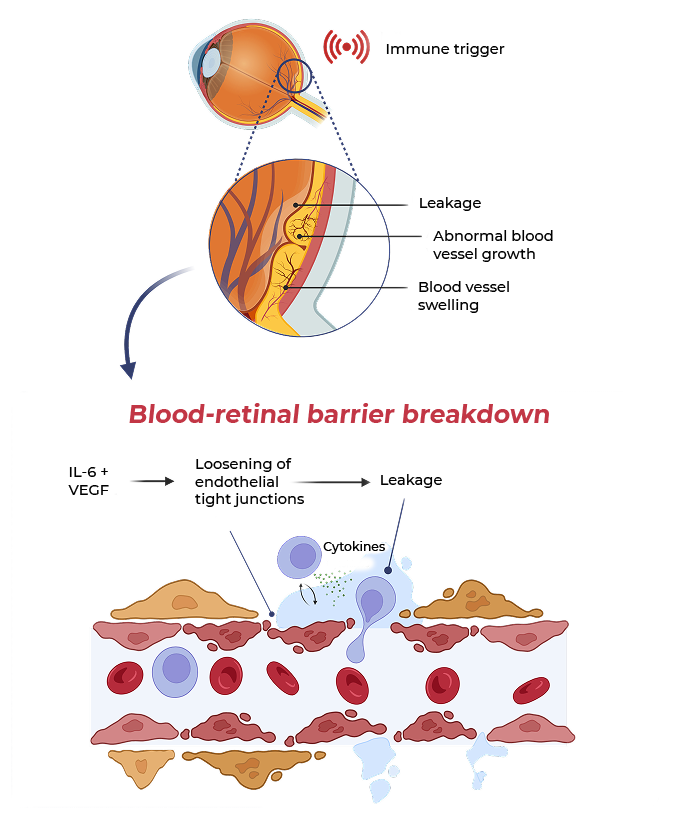
During this process, IL-6 and VEGF are co-induced. IL-6 sustains inflammation and upregulates VEGF, which promotes vascular leak and neovascularization. Together, IL-6 and VEGF compound the damage to the blood-retinal barrier
Signaling
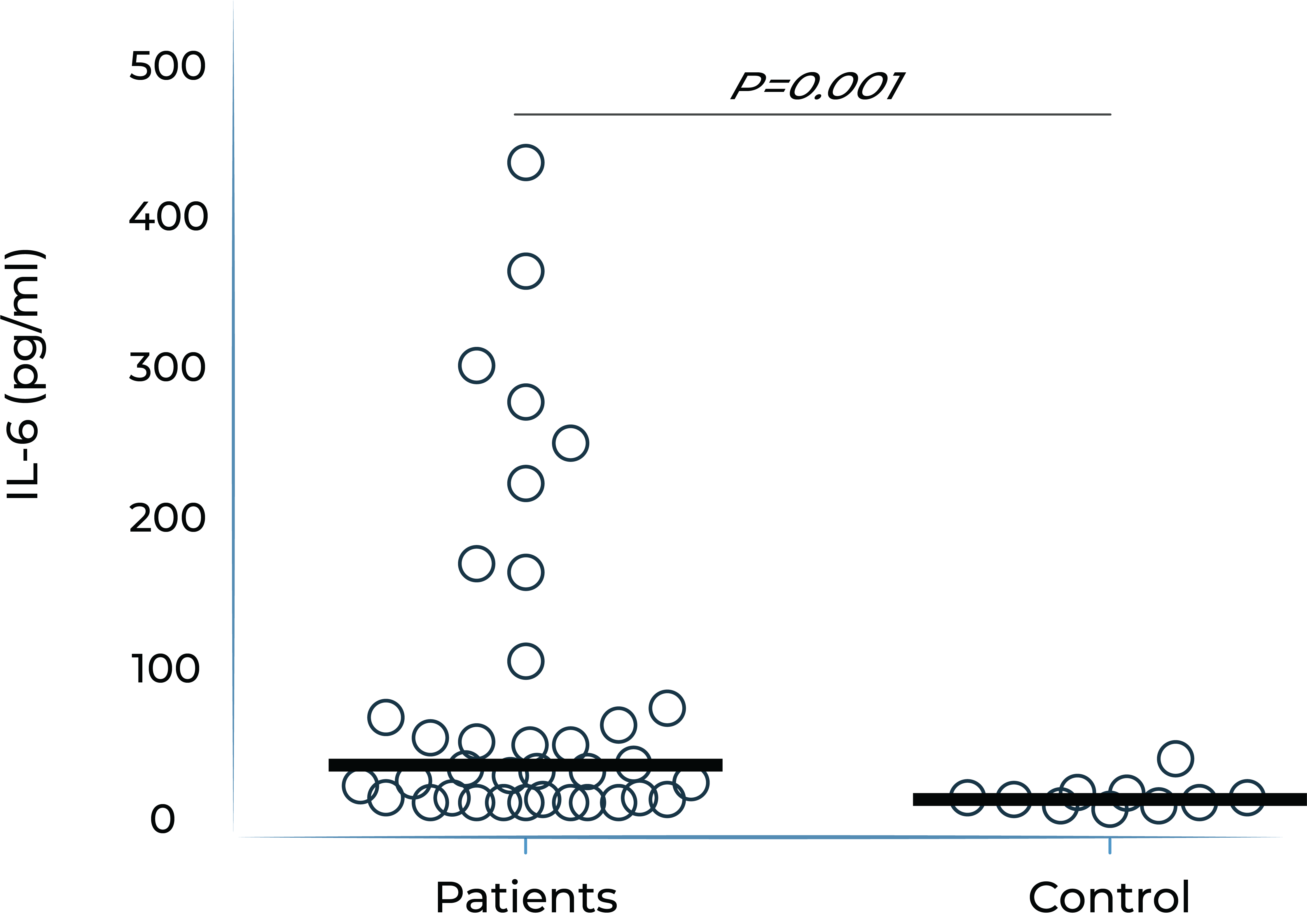
Both IL-6 and VEGF levels are elevated in inflammatory macular edema
Aqueous humor IL-6 levels were elevated in patients with intermediate uveitis
VEGF levels in aqueous humor of uveitis patients with macular edema vs without macular edema
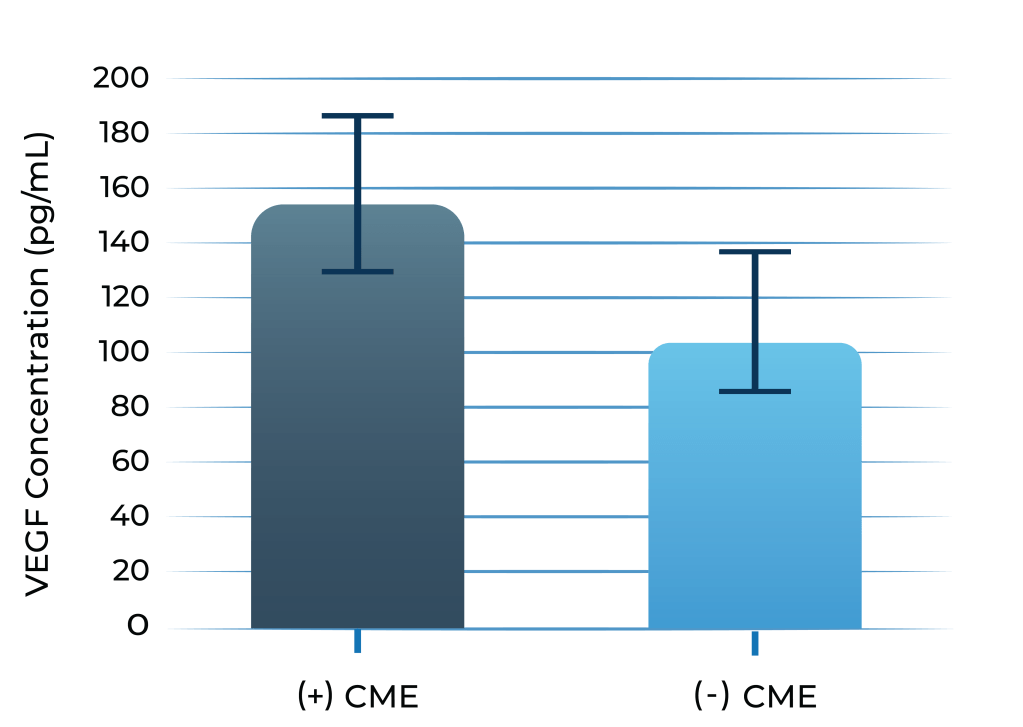
1. Valentincic et al. Molecular Vision 2011; 17: 2003-2010
2. de Boer et al. Curr Eye Res. 1992;11 Suppl:181-186
In a pre-clinical study, bispecific KSI-101 restores blood-retinal barrier integrity more effectively than IL-6 or VEGF inhibitors alone
In a pre-clinical model of endothelial cells simulating the blood-retinal barrier, KSI-101 restores barrier integrity to no exposure levels
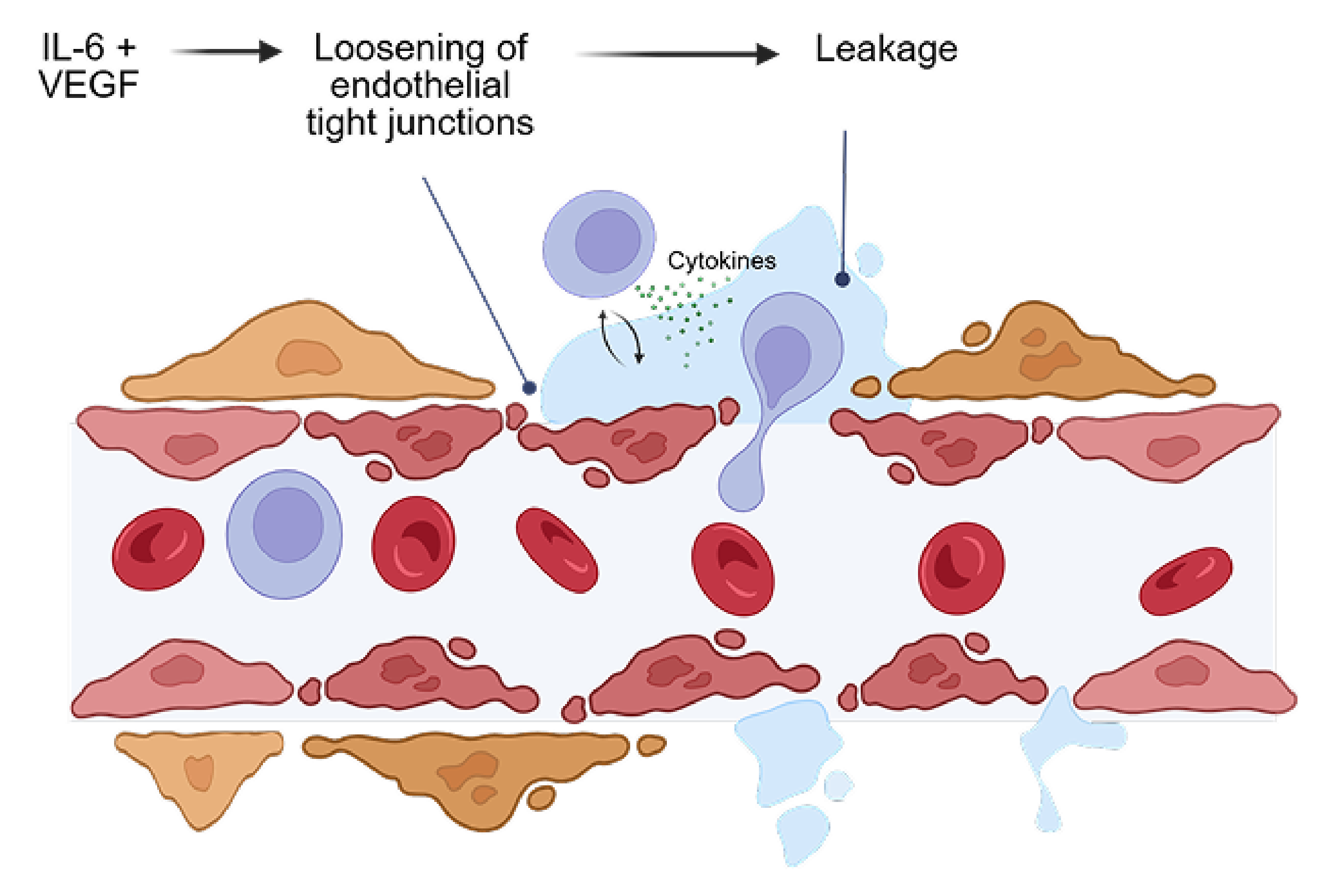
Blood-retinal barrier exposed to VEGF and IL-6
KSI-101 is actively enrolling patients in the Phase 3 PEAK and PINNACLE studies
The APEX Phase 1b study demonstrates that KSI-101 provides meaningful visual and anatomical gains in both DME and MESI and that KSI-101 is well tolerated
See interim APEX Phase 1b results
Meaningful treatment responses were seen in the MESI population, irrespective of the location of inflammation and specific MESI etiology, opening up the potential for KSI-101 to become a unifying treatment for this patient population
|
Phase 1b APEX Study Diabetic Macular Edema Macular Edema Secondary |
|
The KSI-101 program is accelerating based on the positive results of APEX. The Phase 3 PEAK and PINNACLE studies are actively enrolling. PEAK and PINNACLE are superiority studies designed to enroll complementary patient populations and to cover a wide spectrum of MESI patients
|
Phase 3 PEAK & PINNACLE Studies Macular Edema Secondary |
|
Multi-mechanism, multi-modality targeted biologic for complex retinal and systemic diseases
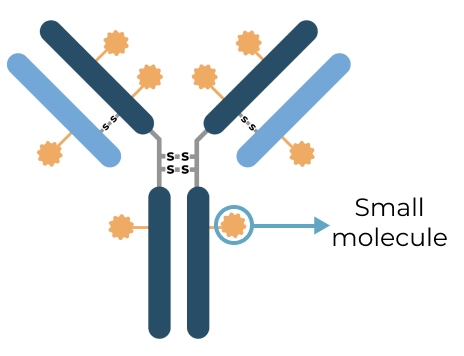
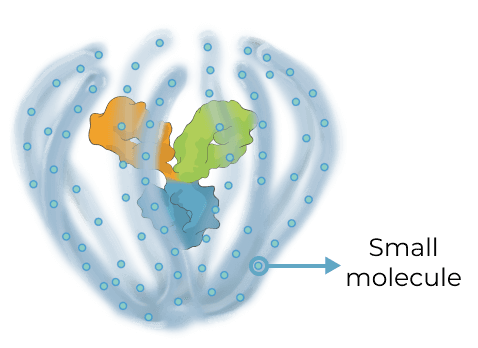
Triplet medicines combine the benefits of our Antibody Biopolymer Conjugate (ABC) Platform for long-interval dosing of biologics with a new feature that adds sustained release of 100s of small molecules to target three or more mechanisms of action, enabling treatment of complex, multifactorial diseases.
Designing a new generation of targeted therapy for high-prevalence multifactorial diseases

Our triplet ABC medicines aim to broaden what’s possible with antibody conjugate therapies
Antibody Drug Conjugate (ADC) therapies are revolutionizing the way cancer is treated today by delivering highly potent cancer-killing agents directly to cancer cells via a targeted antibody. With our ABC triplet medicines, we aim to build on this foundation in notable ways:
ADC
|
ABC Triplet Medicine
|
Our goal with our triplet medicines is to deliver greater therapeutic benefit for multifactorial diseases in the eye and systemically by modulating multiple distinct pathological processes in parallel


.png)